This post was originally intended to be a guide for using my Differentiated Article Sets (available on TPT ^_~), but it can apply to using any texts you have at multiple reading/lexile levels.
JUMP RIGHT TO IMPLEMENTATION SUMMARY
For those who don't know (Hey there, welcome! Hope you enjoy your time here.), I teach high school direct instruction English and Intensive Reading to students with high-incidence disabilities - primarily learning disabilities, language impairments, ADHD, and Autism. The reading skills of my students vary widely (from kindergarten-level to nearly grade-level), so I am constantly differentiating my instruction to meet their needs (or at least trying to).
One easy way to differentiate is to use texts that have been adapted to different levels of complexity. Differentiating texts allows students to engage with the material at a difficulty level they can be successful with, ensuring that all learners can develop their skills effectively.
While you
could probably categorize your students into 10 different levels of
reading ability (I know I can, lol), I typically group students into
three levels. I think this is a manageable number for the teacher, and
it typically works for creating small groups that are large enough to
generate discussion, but small enough to provide students with practice
opportunities and individualized support and feedback.
FINDING TEXTS
While teachers have been told for decades that we need to differentiate our instruction, there's surprisingly few resources for differentiated materials at the secondary level. Most of the differentiated text sets I've found online or on TPT are designed for elementary, or they include texts at different levels that discuss a similar topic, but don't cover the same information. This is fine if you're doing all of your instruction in small groups, but that's not realistic, nor is it ideal. While students can do some deep learning in leveled groups, they also benefit from mixed-ability groups and whole group instruction.
In order to differentiate in those settings, you need texts about the same topic at different instructional levels. The best-known source for this in secondary (at least in my experience) is Newsela. Newsela provides a variety of texts including (relatively) recent events. You can find some really interesting topics on there, and the texts are offered at up to five reading levels. They also include comprehension questions and writing prompts. If you're never tried it, I suggest you check it out. They have a paid version (I'm lucky enough that my district provides this) and a "Freemium" version.
While I do use Newsela, I typically only use it in small groups. Reason being that when they lower the levels of their articles, they tend to remove information and even entire sections. They also completely change the questions. This is fine in small group but makes any whole group discussion difficult and cumbersome (which kind of defeats the point of everyone reading about the same topic). I also find students get frustrated by the length of these articles and avoid completing them independently.
ReadWorks
also provides some of their texts in differentiated levels in their
StepReads category. I haven't spent a lot of time looking through these,
mainly because most of the texts I checked only offered one lowered
level of the text that was still pretty high in text complexity, so it
doesn't work for my needs. I do like that they try to keep the same text
structure, vocabulary, and content, but I think that hinders their
ability to differentiate widely.
In researching for this article, I came across the website For the Teachers which offers texts at three different reading levels. They also list related skills for each text which I like since I often structure my curriculum around targeting specific reading skills (although I couldn't find anywhere that they provide any actual questions for the texts). It looks like there could be some good materials here, but I am concerned about their statement "These articles are fiction, but they are written to be read and used as non-fiction." Given the prevalence of false information these days, I don't understand why they would go this route. I also ran into issues of broken or incorrect links which would be very frustrating to deal with if I was trying to get resources together for a unit.
If you want to check out more resources, including some for elementary and some targeted to ELLs, Larry Ferlazzo offers a comprehensive list here.
Now I would be remiss if I didn't mention the differentiated article sets I've made. I created these because I couldn't find the resources I needed for my students. I was looking for articles that:
- Were available at multiple reading levels
- Were about interesting topics
- Covered the same key content in each article
- Included questions that could be applied across all levels of texts
My goal was to be able to provide my students with texts that were targeted to their instructional level, without making the difference obvious to other students in the class. Even when everyone is in the class because they struggle with reading, they still get embarrassed when they are given "easier" work than their peers.
My articles
include three versions of the text (approximately 3rd, 6th, and 9th
grade levels), four levels of text-dependent questions (including
multiple choice and open response), and personal response questions.
They're pretty cheap at only $3 too. If you think you might be
interested, you can check them out here.
IMPLEMENTATION
Alright
so you've found your articles. Now, how do you use them? There are a
number of different ways, but I'll outline the four I use most often
here. But first a quick aside about learner profiles
The Importance of Learner Profiles
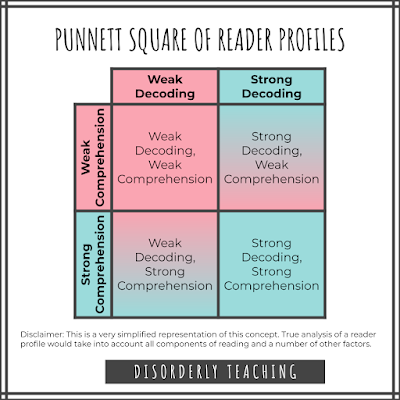
When implementing differentiated reading strategies, it is crucial to consider each student's unique learner profile. This means taking into account their abilities with all components of the reading process. With my students I focus mainly on decoding and comprehension. I kind of view it like a Punnett Square (remember those from high school?).
Based on this we end up with four learner profiles. If you stop here, you can essentially make three levels of groups: students who are weak in both areas, students who are weak in one area, and students who are strong in both areas. In this case you can simply provide each of the three levels with three tiers of articles and questions.
In my article sets, you can use the quick print guide to do just that!
Method 1: Independent Reading with Targeted Texts and Questions
Assign texts according to each student's reading level, allowing them to work independently. This approach gives students the opportunity to practice their decoding and comprehension skills at a comfortable level of difficulty, fostering growth and confidence in their abilities.
Your goal is for each student to feel challenged and supported. You can assign specific texts to students, or you can allow students to choose which one best suits their needs, promoting self-determination.
While differentiated articles work great for independent skill practice, they can also be excellent resources for working with students in small groups. In fact, it was working with my small groups that first inspired me to find leveled texts with similar content and skill practice.Method 2: Small Group Reading for Targeted Support
For classrooms with diverse reading levels, small group instruction is crucial. This method allows for targeted instruction and support, ensuring that struggling students receive the necessary scaffolding to develop their skills. This method not only caters to the individual needs of each student, but also fosters a sense of community as students work together towards shared learning goals.
You can meet with all three leveled groups, but it's okay to sometimes let your higher-level readers work independently, while you work with lower-level readers. Struggling students need more direct instruction to build foundational skills and to ensure they are not practicing and reinforcing errors.
But Tracy, you say, I want to review the comprehension questions with all of my students, but I don't have enough time to meet with them all in small groups. How can I give them differentiated texts to read, but still review the questions together?Method 3: Whole Group Discussion with Targeted Texts and Unified Questions
Our third strategy is to provide students with differentiated texts but assign the same set of questions. This approach allows learners at different reading levels to engage with the material in a meaningful way while still promoting critical thinking and comprehension skills. By using the same question set, students can participate in discussions and collaborate with their peers, regardless of their individual reading abilities.
If
you use this method I would suggest using Level 2 multiple choice
questions. Use whatever will best serve the needs of your students. If
you worry that some students will struggle with the level of questions
you chose to use, you can try having students work in pairs, rather than
individually. If a student has strong decoding skills but struggles
with comprehension, try pairing them with a peer who has strong
comprehension skills and a weakness in decoding. They can work together
to make sense of the text, discuss their ideas, and learn from one
another.
But what if you have a greater variety of learners in your class and still want them to be able to work independently? Perhaps you have a student with strong decoding skills but very weak comprehension. If you give them a Level 2 set, they won't be challenged by reading the text, and the questions may be too difficult for them to answer.
This is where mixing and matching comes in.
Let's take our Punnet Square and further differentiate it by adding a third level for each.
Method 4: Mixing and Matching
There is no rule that says you have to use Level 2 questions with a Level 2 text. Mix and match articles and question sets to your hearts content. For example I have a student with decent comprehension skills but very weak writing skills (plus large handwriting!). I give him standard multiple choice text-dependent questions, but give him wide lined personal response questions.
You have to gauge your students to
know which material is best for which student. Simple guidelines would
be to base the text level on their decoding skills and the question
level on their comprehension skills. From there you can fine tune as
necessary.
- Using Differentiated Texts and Questions
- Four Main Methods
- Independent Reading with Targeted Texts and Questions
- Small Group Reading for Targeted Support
- Whole Group Discussion with Targeted Texts and Unified Questions
- Mixing and Matching
- Using Disorderly Teaching Differentiated Article Sets
- Articles can be used for any of the methods above
- The sets were originally designed to allow for whole group discussion
- You can further differentiate by having higher level students read independently while you read the article together with lower level students in a small group.
- Each article contains the same key information so that the content can be discussed in a whole group lesson.
- Levels
are marked with a small code on the corner of the page. These codes are
used to mask the level information so it's not as obvious to students.
- The codes are listed in the Table of Contents (p. 3).
- The last letter of the code indicates the level.
- Level 1 = a
- Level 2 = b
- Level 3 = c
- The question sets are all worded the same way and cover the same skills and content, but are differentiated in response type.
- Questions can be reviewed in whole group, but it would then become obvious that some students have questions presented differently from others. There is nothing wrong with this, but you know your students and how they would handle this best.
- If you think this may be an issue, you can
give students differentiated articles but give them all the same
question set. In this case I would suggest using either the multiple
choice questions with 4 choices, or open response with lines. Use
whatever will best serve the needs of your students.